What is a Semiconductor Cleanroom?
A semiconductor cleanroom is a highly controlled environment specifically designed to minimise contamination and ensure the high-quality production of semiconductor devices, such as microchips.
These cleanrooms are essential in the semiconductor manufacturing processes. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity must be closely controlled, and even tiny particles such as dust or other contaminants can significantly impact the effect and reliability of these highly sensitive electronic components.
In this blog, we’ll aim to explain the key features of semiconductor cleanrooms, their applications and relevant classifications.
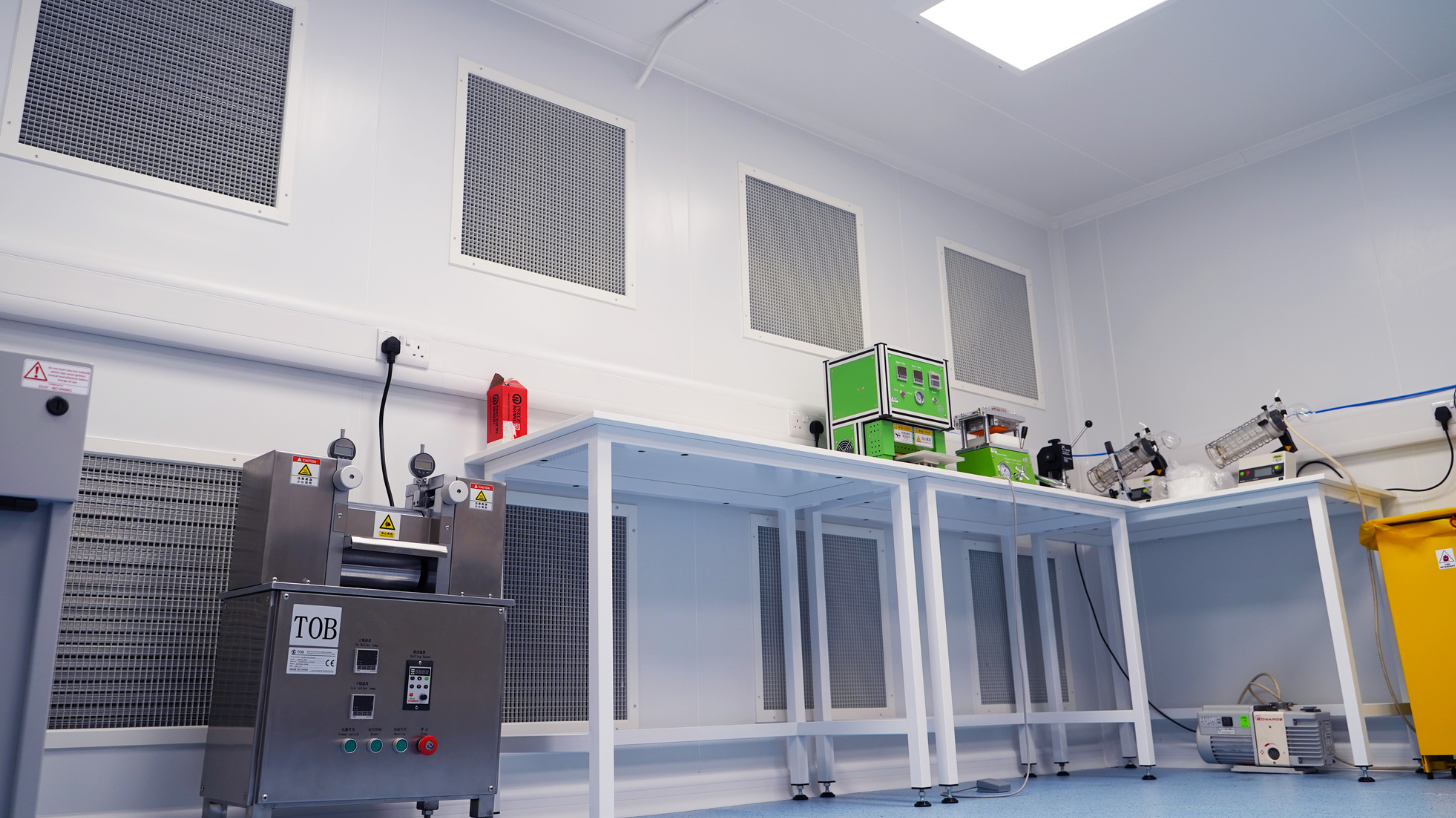

What are Semiconductors?
Before we go into the detail of semiconductor cleanrooms, it’s important to understand what exactly a semiconductor is! Defined by the Semiconductor Industry Association, a semiconductor is:
“An essential component of electronic devices, enabling advances in communications, computing, healthcare, military systems, transportation, clean energy, and countless other applications.”
Reference: Semiconductor Industry Associated, ‘what is a semiconductor?’
How are Semiconductors Made?
Made using a glassy, solid material of pure silicon which is shaped whilst in a molten state and cut into thin wafers, semiconductors are esteemed for their conductive behaviour; they behave both like a metal and an insulator which is a vital ingredient for manufacturing computer chips and circuitry. The wafer element mentioned above is a substrate that’s then used for either a chip or integrated circuit.
Semiconductor chips are extremely fragile, and even the slightest defect or inconsistency can compromise its safety and effectiveness, which in turn can ultimately compromise the safety and effectiveness of the machines and equipment which are powered by those chips. This is why semiconductor cleanrooms are so important, and why they must comply with strict standards to ensure total control and compliance in the chip manufacturing environment.
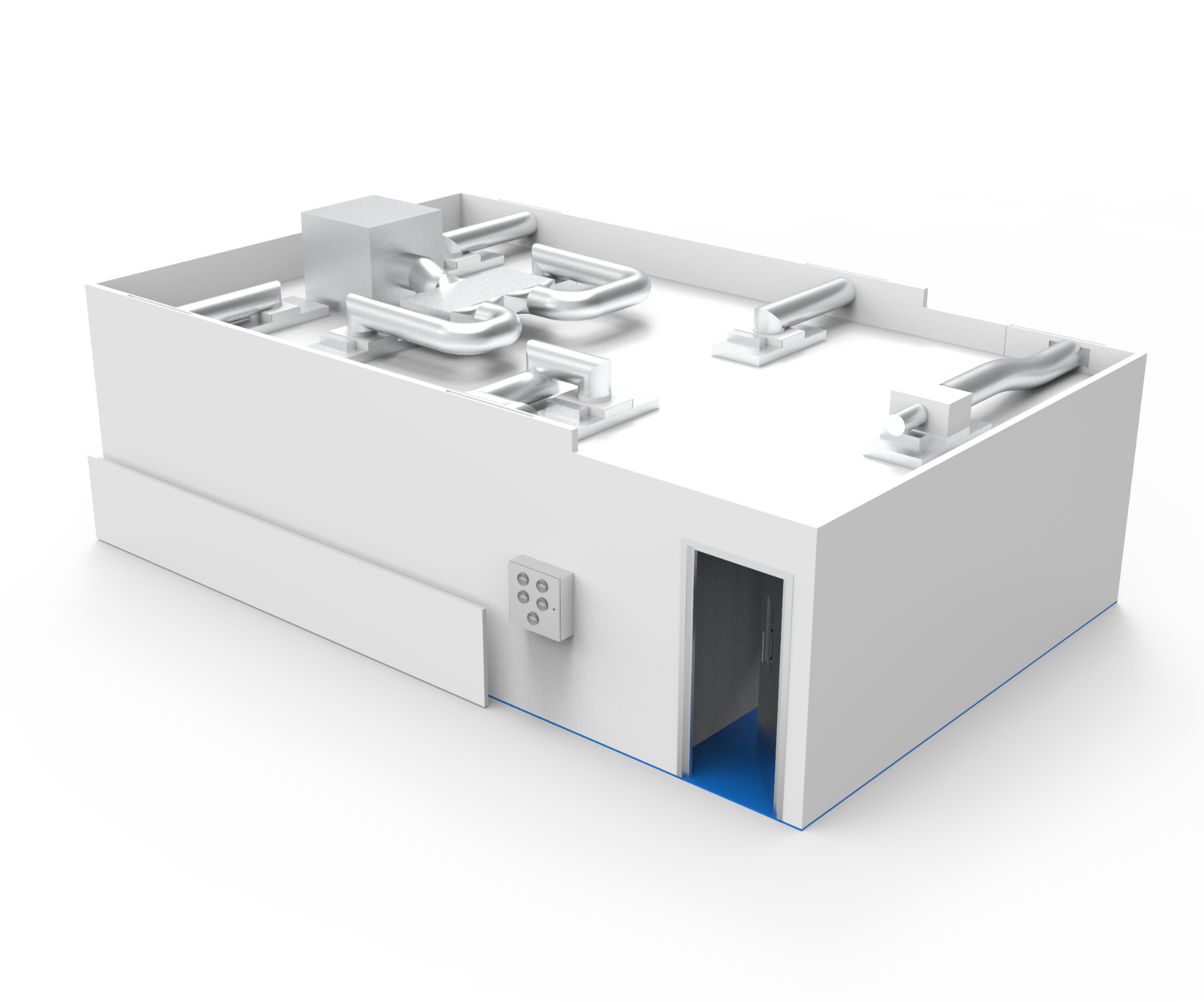
Key Features of Semiconductor Cleanrooms

Controlled Environment

Filtration System

Classifications
Strict Protocols & Procedures

Airflow
Material Compatability
Semiconductor Applications
The need for cleanroom environments arises when working with sensitive electronic components or processes that demand a controlled atmosphere to ensure high-quality production and performance. Examples of applications that may require a semiconductor or electronics cleanroom include:
- Semiconductor manufacturing: Cleanrooms are crucial for producing integrated circuits (ICs), microchips and other semiconductor devices. They provide a controlled environment free from dust, particles and other contaminants that could adversely affect fabrication.
- Lithium battery manufacturing: Humidity control is critical in battery dry rooms as various materials and processes used in battery production are susceptible to moisture damage.
- Microelectronics assembly: Cleanrooms are used to assemble and pack microelectronic components such as chips, sensors and transistors. These delicate components require a clean environment to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
- Flat panel display manufacturing: The production of LCD (liquid crystal display) OLED (organic light-emitting diode), and other flat panel displays require cleanroom facilities to ensure the manufacturing process remains free from dust and other contaminants.
- Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS): MEMS devices, which combine mechanical and electrical components on a small scale, often require cleanroom facilities for their cleanroom fabrication. Examples include accelerometers, pressure sensors and microfluid devices.
Semiconductor Cleanroom Classifications
Due to the fragility and end use of semiconductors, some of the most stringent cleanroom classifications must be maintained consistently throughout the manufacturing process.
In most cases, semiconductor cleanrooms must comply with ISO 14644-1 Class 5-8 requirements, however not all processes require such stringent control. The packaging, assembly and testing of manufactured semiconductors could be performed in ISO Class 7 or ISO Class 8 cleanrooms, for example.
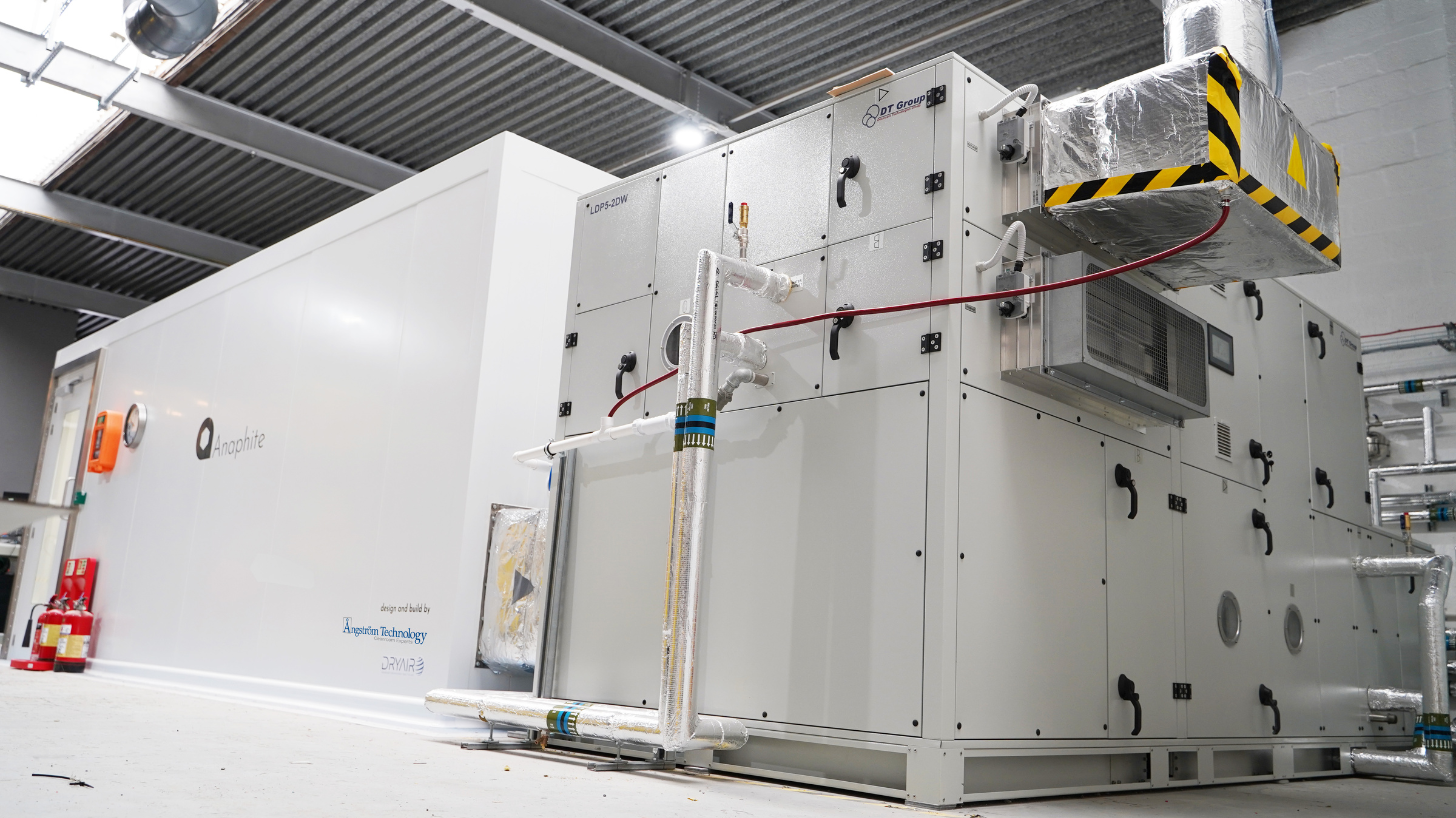
Battery dry rooms require a constant supply of ultra-dry air to create and maintain low-humidity conditions for the R&D and production of solid-state and lithium-ion batteries.
We can develop an energy-efficient dry room to protect your critical process by combining airtight envelope systems, dehumidification systems and HVAC design.
For more information about dry rooms, click here to download our Dry Room Design Guide.
To find out more about cleanroom classifications, click here.
The Importance of Cleanrooms in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Efficient Yield: The cleanliness of the manufacturing environment is directly related to the yield of functional semiconductor devices. Higher yields mean that more devices meet quality standards and wider demand, reducing waste and increasing profitability.
Quality Control: Ensuring a contaminant-free environment is crucial for the consistent performance and reliability of semiconductors, which are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices and automotive systems.
Innovation and Advancement: As semiconductor technology advances, the size of transistors and other components on a chip continues to shrink, requiring even cleaner environments to prevent defects. Cleanrooms enable the production of advanced technologies like microprocessors and memory chips with extremely small geometrics.
Summary
Semiconductor cleanrooms are specialised facilities that ensure the controlled environment necessary for the precise and contamination-free manufacturing of semiconductor devices. They are critical to maintaining the high standards required in the semiconductor industry for both quality and innovation; here at Connect 2 Cleanrooms we have a wealth of experience in designing, building and maintaining semiconductor cleanrooms, so be sure to read our case studies and contact us about your next project!


START A PROJECT WITH US
Our design and build specialists have experience working with customers in all kinds of industries on a global scale, achieving great results time and time again. We’d love to work with you too!




